Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawaguchi, Koichi; Segawa, Tomoomi; Ishii, Katsunori
Funtai Kogakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.283 - 290, 2022/06
In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in order to effectively use the out-of-standard pellets in the fuel manufacturing process for high-speed furnaces, we are developing techniques for crushing and reusing them with raw material powder. By analyzing in detail the particle size distribution before and after grinding, it was shown that the grinding powder is composed of three different component particles having different characteristics of the particle size distribution. In addition, we examined the method of predicting pulverized powder particle size distribution from the supply powder particle size distribution.
Miyahara, Shinya*; Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Seino, Hiroshi; Atsumi, Takuto*; Uno, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/08
In a postulated accident of fuel pin failure of sodium cooled fast reactor, a fission product cesium will be released from the failed pin as an aerosol such as cesium iodide and/or cesium oxide together with a fission product noble gas such as xenon and krypton. As the result, the xenon and krypton released with cesium aerosol into the sodium coolant as bubbles have an influence on the removal of cesium aerosol by the sodium pool in a period of bubble rising to the pool surface. In this study, cesium aerosol removal behavior due to inertial deposition, sedimentation and diffusion from a noble gas bubble rising through liquid sodium pool was analyzed by a computer program which deals with the expansion and the deformation of the bubble together with the aerosol absorption considering the effects of particle size distribution and agglomeration in aerosols. In the analysis, initial bubble diameter, sodium pool depth and temperature, aerosol particle diameter and density, initial aerosol concentration in the bubble were changed as parameter, and the results for the sensitivities of these parameters on decontamination factor (DF) of cesium aerosol were compared with the results of the previous study in which the effects of particle size distribution and agglomeration in aerosols were not considered. From the results, it was concluded that the sensitivities of initial bubble diameter, the aerosol particle diameter and density to the DF became significant due to the inertial deposition of agglomerated aerosols. To validate these analysis results, the simulation experiments have been conducted using a simulant particles of cesium aerosol under the condition of room temperature in water pool and air bubble systems. The experimental results were compared with the analysis results calculated under the same condition.
Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Iida, Takao*; Sato, Kaoru; Tsuda, Shuichi
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 56(4), p.615 - 620, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.41(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Formation mechanism and size distribution of radioactive aerosol particles generated in a high-energy neutron field were studied in order to evaluate a particle size parameter for internal dose evaluation in high-energy accelerator facilities. Argon gas containing DOP aerosols was irradiated by a 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutron beam of TIARA. The number size distribution of the DOP aerosols and the activity-weighted size distribution of  Cl and
Cl and 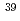 Cl aerosols, formed from the (n, 2np) and (n, np) reactions of
Cl aerosols, formed from the (n, 2np) and (n, np) reactions of  Ar, were measured using an electrical low-pressure impactor. The activity-weighted size distribution of the radioactive aerosols was well explained by the simple attachment model of the radioactive atoms to the DOP aerosols.
Ar, were measured using an electrical low-pressure impactor. The activity-weighted size distribution of the radioactive aerosols was well explained by the simple attachment model of the radioactive atoms to the DOP aerosols.
; Ikezawa, Yoshio
Hoken Butsuri, 25(3), p.294 - 298, 1990/00
no abstracts in English
; ;
JAERI-M 84-235, 44 Pages, 1985/01
no abstracts in English
*; ;
JAERI-M 82-141, 74 Pages, 1982/10
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 11(11), p.510 - 515, 1974/11
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
 pellet in air; Effect of heat-treatment of pellet on particle size distribution of powders produced
pellet in air; Effect of heat-treatment of pellet on particle size distribution of powders produced; ; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 5(12), p.652 - 653, 1968/00
Times Cited Count:14no abstracts in English